Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) is a middleware tool provided by Oracle that enables you to easily expose Oracle Database data and logic as RESTful web services. It’s a key component for modern application development, allowing seamless integration of database functionality with web, mobile, and cloud applications.
ORDS (Oracle REST Data Services) is a Java-based application that acts as a bridge between HTTP(S) clients and Oracle Databases. It allows developers to interact with the database using REST APIs instead of traditional SQL or PL/SQL over JDBC or SQL*Net.
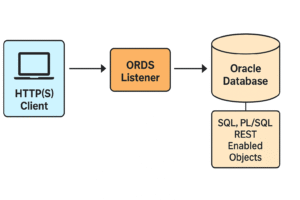
ORDS acts like a lightweight web server that interprets HTTP requests, connects to the Oracle DB, executes the logic, and returns responses in JSON.
Key Features of ORDS:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| 🔁 REST Enablement | Turn SQL queries, PL/SQL blocks, or database objects into REST APIs. |
| 📱 Mobile Friendly | Build APIs for web/mobile/cloud without writing backend code repeatedly. |
| 🧩 APEX Integration | ORDS is the web listener for Oracle APEX, making it work over HTTP/HTTPS. |
| 🔐 Security | Supports OAuth2, Basic Auth, and integration with Oracle Identity solutions. |
| ⚙️ Easy Deployment | Runs on Java application servers like Tomcat, Jetty, or standalone mode. |
| 📂 File Uploads | Supports BLOB data access (images, PDFs, etc.) through REST. |
We can achieve below things using ORDS:
Expose Database Tables as REST Endpoints:
Example: GET /ords/hr/employees/
This will return employee data from the HR. EMPLOYEES table.
Run SQL Queries via REST:
Define a SQL query or PL/SQL block and expose it as a GET/POST endpoint.
Create, Update, Delete Rows:
Use POST/PUT/DELETE to interact with your tables via REST—like a mini backend.
Manage Oracle APEX:
ORDS is the web interface for Oracle APEX apps.
How ORDS works Internally?
- ORDS is deployed on a web server (like Tomcat or as a standalone Java app).
- It connects to Oracle Database schemas using JDBC.
- You define REST modules, templates, and handlers in the database via SQL Developer or PL/SQL.
- ORDS processes the REST call, executes the database logic, and returns the result in JSON.
Security in ORDS:
Basic Authentication: HTTP Basic Auth with database users.
OAuth2 Support: Create clients, access tokens, and scopes.
Role-based Access: Secure endpoints using role mappings.
When to use ORDS?
Use ORDS if:
- You want to expose database functionality over the web.
- You’re building mobile/web apps that need backend APIs.
- You use Oracle APEX or work with Oracle Fusion middleware.
- You want lightweight API access without a heavy application server.
