In this post, we will see how to use SELECT AI for Oracle Autonomous Database in 23AI.
SELECT AI is a new feature introduced in Oracle Database 23ai (formerly Oracle Database 23c) that integrates natural language processing (NLP) directly into SQL, enabling users to query the database using plain English or other natural languages.
SELECT AI allows users to write natural language queries, and the database automatically translates them into SQL statements using integrated AI models and large language models (LLMs).
Follow steps below to setup and use SELECT AI in ATP 23AI Database.
Provision ATP database in oracle cloud infrastructure.
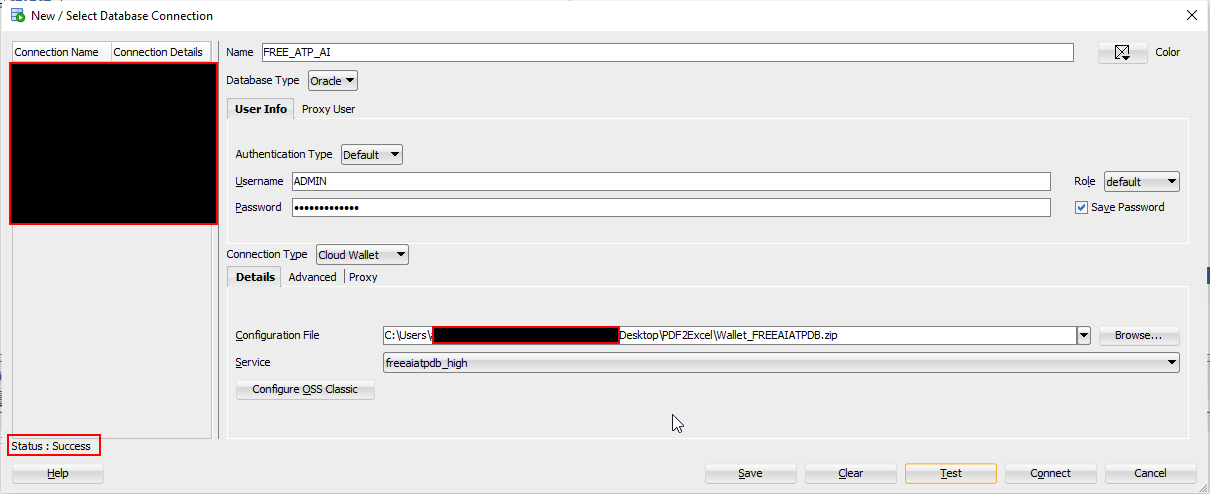
Download wallet and upload it to SQL developer to connect.
Refer (How to Provision ATP Database in OCI and connect from SQL developer) post for more details.
Use ADMIN user with which we have provision ATP database in OCI.
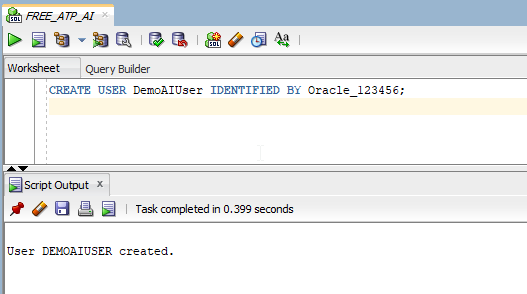
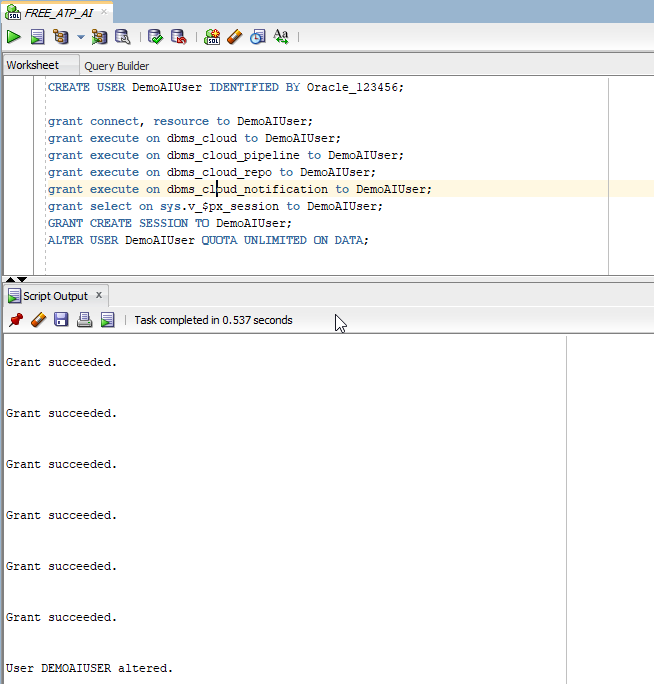
Create new user with username as DemoAIUser.
CREATE USER DemoAIUser IDENTIFIED BY Oracle_123456;
Execute below statement to provide grants to DEMOAIUSER.
grant connect, resource to DemoAIUser; grant execute on dbms_cloud to DemoAIUser; grant execute on dbms_cloud_pipeline to DemoAIUser; grant execute on dbms_cloud_repo to DemoAIUser; grant execute on dbms_cloud_notification to DemoAIUser; grant select on sys.v_$px_session to DemoAIUser; GRANT CREATE SESSION TO DemoAIUser; grant execute on dbms_cloud_ai to DemoAIUser; ALTER USER DemoAIUser QUOTA UNLIMITED ON DATA;
Result:
We are going to use cohere as LLM provider. To access LLM rest API from 23AI database, we need provide ACL access.
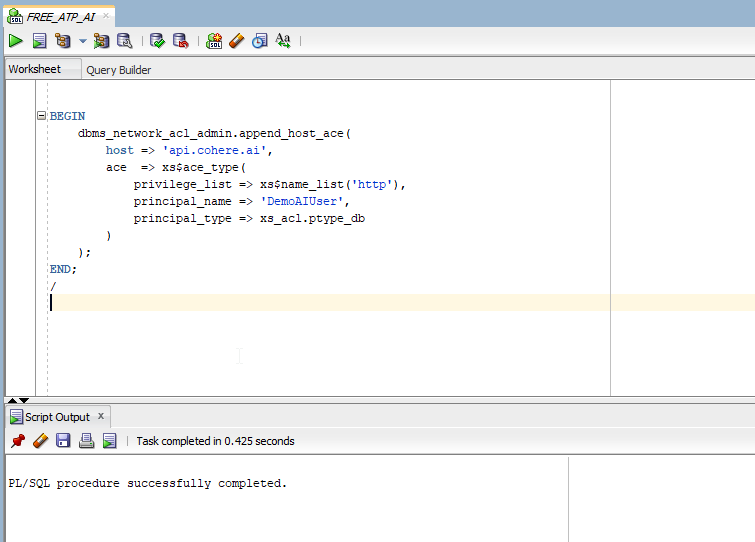
Execute below PLSQL block.
BEGIN dbms_network_acl_admin.append_host_ace( host => 'api.cohere.ai', ace => xs$ace_type( privilege_list => xs$name_list('http'), principal_name => 'DemoAIUser', principal_type => xs_acl.ptype_db ) ); END; /
Login with DemoAIUser from SQL developer.
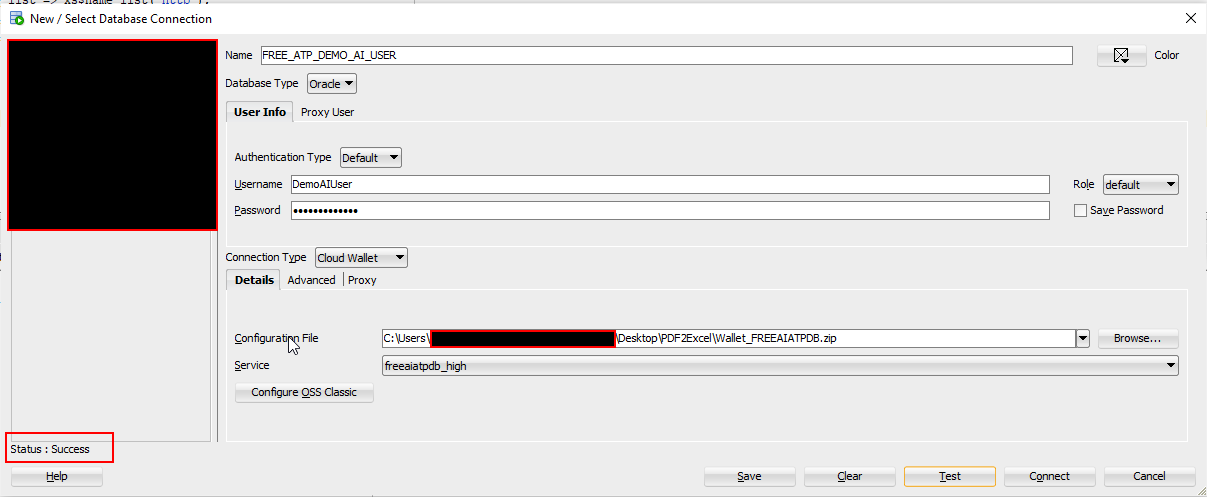
Click on Save and then connect.
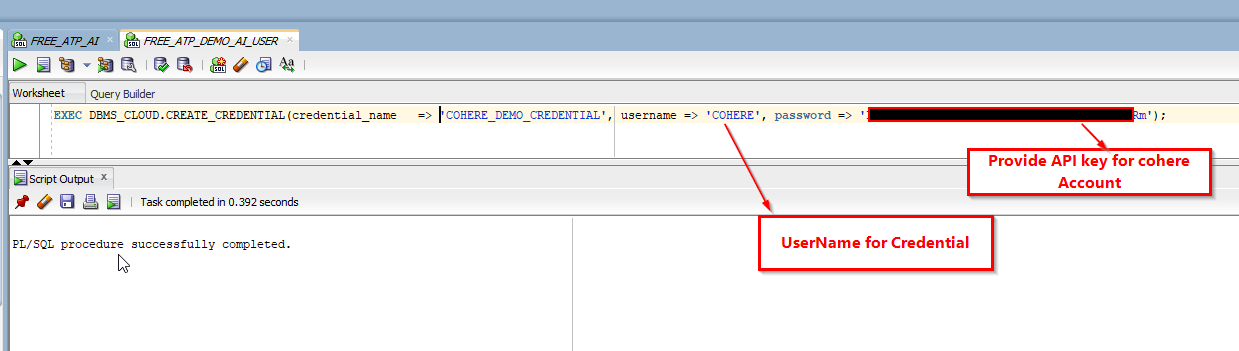
Create credentials to connect to cohere using cohere API key.
Execute below SQL Statement:
EXEC DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL(credential_name => 'COHERE_DEMO_CREDENTIAL', username => 'COHERE', password => 'XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX');
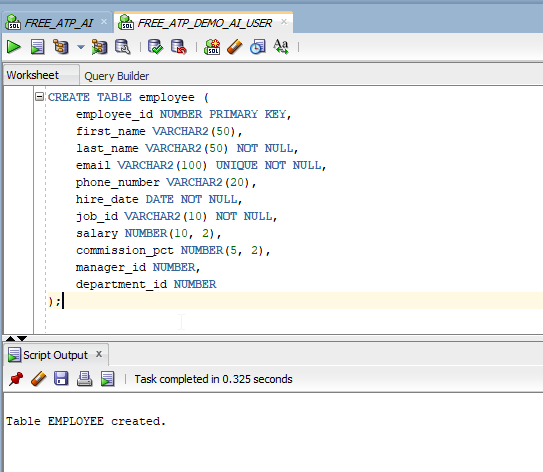
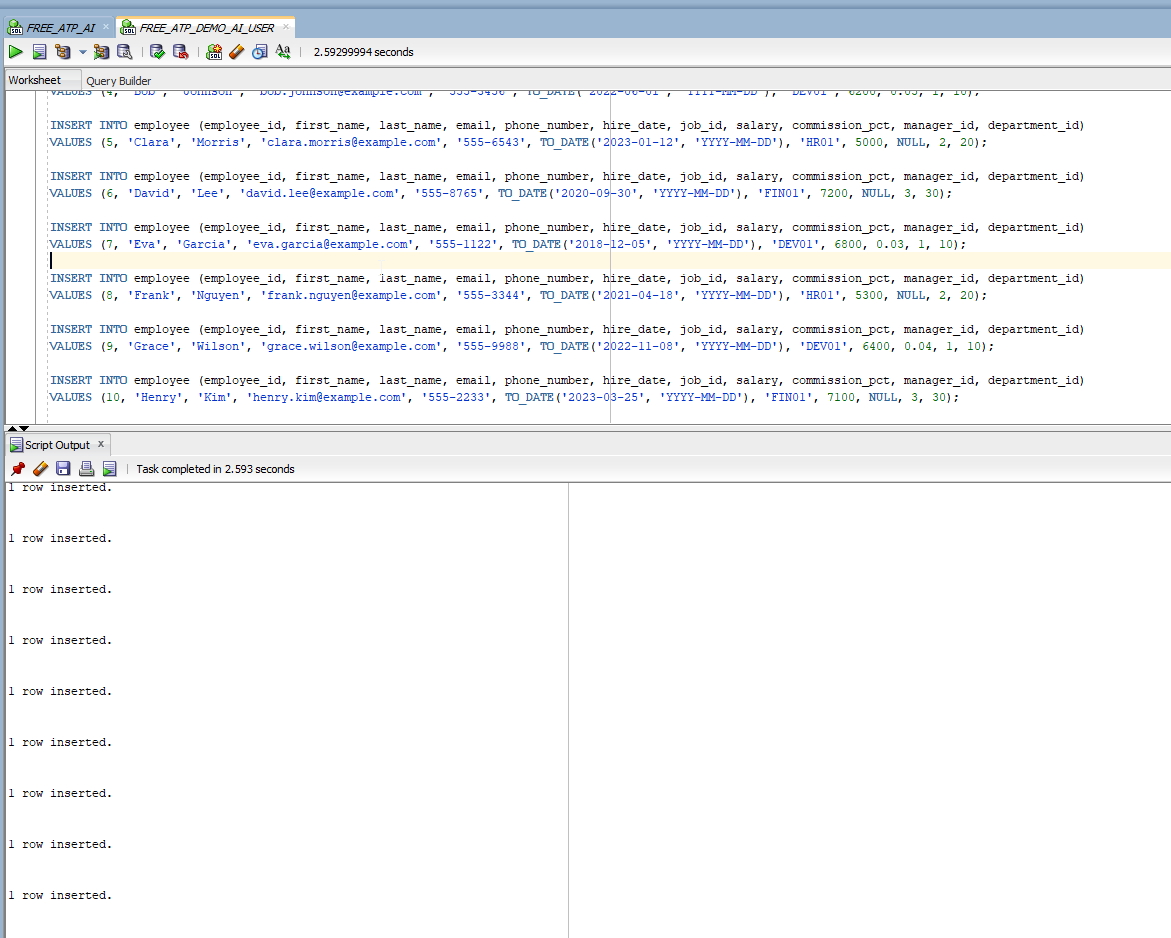
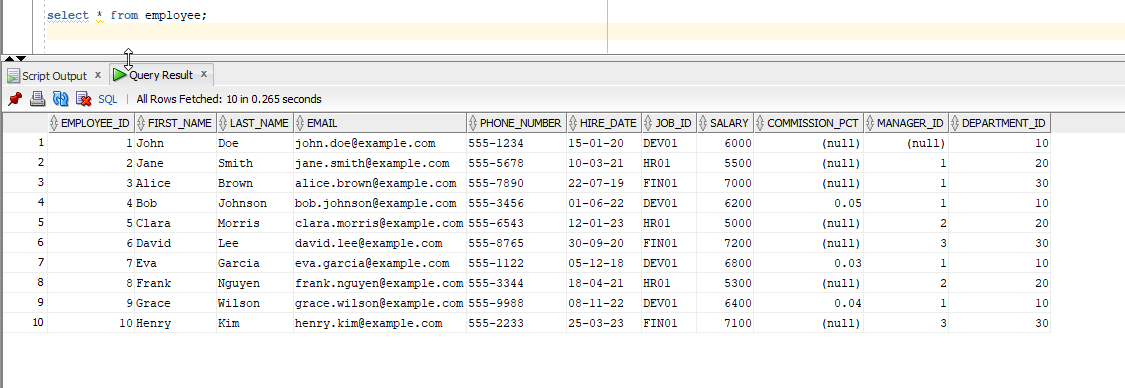
Create Employee table as shown below with data into DemoAIUser schema.
CREATE TABLE employee ( employee_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY, first_name VARCHAR2(50), last_name VARCHAR2(50) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR2(100) UNIQUE NOT NULL, phone_number VARCHAR2(20), hire_date DATE NOT NULL, job_id VARCHAR2(10) NOT NULL, salary NUMBER(10, 2), commission_pct NUMBER(5, 2), manager_id NUMBER, department_id NUMBER ); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (1, 'John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com', '555-1234', TO_DATE('2020-01-15', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'DEV01', 6000, NULL, NULL, 10); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (2, 'Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com', '555-5678', TO_DATE('2021-03-10', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'HR01', 5500, NULL, 1, 20); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (3, 'Alice', 'Brown', 'alice.brown@example.com', '555-7890', TO_DATE('2019-07-22', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'FIN01', 7000, NULL, 1, 30); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (4, 'Bob', 'Johnson', 'bob.johnson@example.com', '555-3456', TO_DATE('2022-06-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'DEV01', 6200, 0.05, 1, 10); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (5, 'Clara', 'Morris', 'clara.morris@example.com', '555-6543', TO_DATE('2023-01-12', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'HR01', 5000, NULL, 2, 20); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (6, 'David', 'Lee', 'david.lee@example.com', '555-8765', TO_DATE('2020-09-30', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'FIN01', 7200, NULL, 3, 30); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (7, 'Eva', 'Garcia', 'eva.garcia@example.com', '555-1122', TO_DATE('2018-12-05', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'DEV01', 6800, 0.03, 1, 10); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (8, 'Frank', 'Nguyen', 'frank.nguyen@example.com', '555-3344', TO_DATE('2021-04-18', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'HR01', 5300, NULL, 2, 20); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (9, 'Grace', 'Wilson', 'grace.wilson@example.com', '555-9988', TO_DATE('2022-11-08', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'DEV01', 6400, 0.04, 1, 10); INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (10, 'Henry', 'Kim', 'henry.kim@example.com', '555-2233', TO_DATE('2023-03-25', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 'FIN01', 7100, NULL, 3, 30);
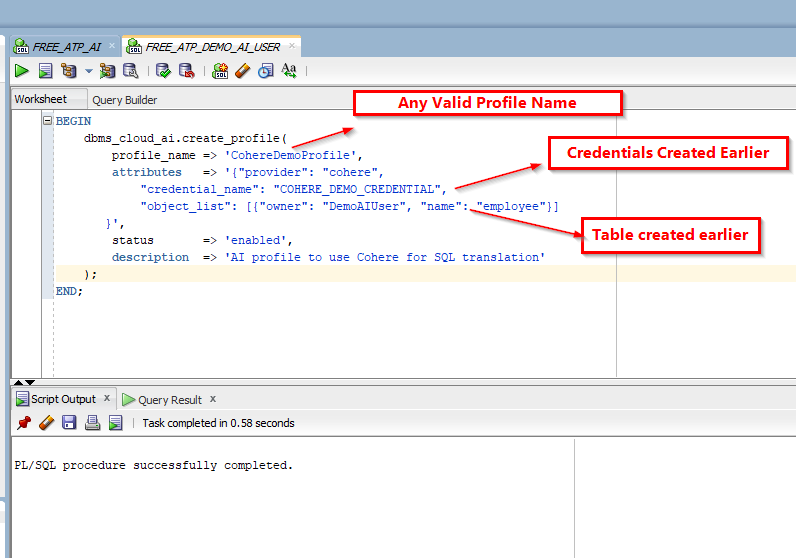
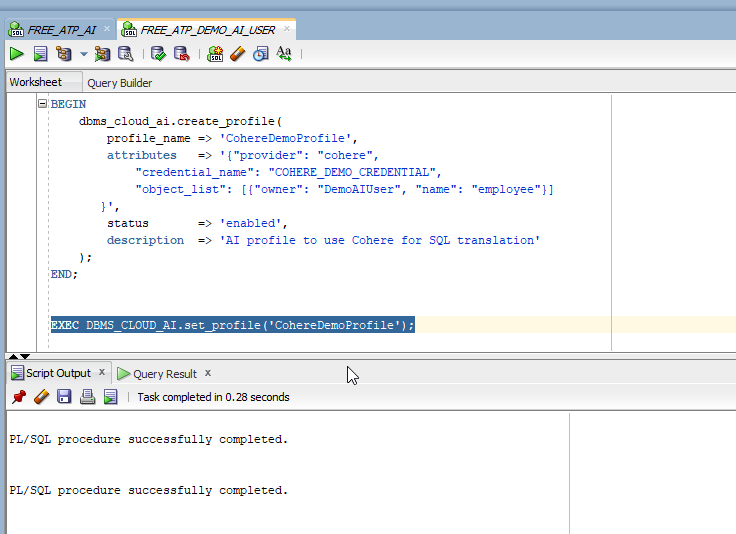
Create Select AI profile:
Run below SQL statement as:
BEGIN dbms_cloud_ai.create_profile( profile_name => 'CohereDemoProfile', attributes => '{"provider": "cohere", "credential_name": "COHERE_DEMO_CREDENTIAL", "object_list": [{"owner": "DemoAIUser", "name": "employee"}] }', status => 'enabled', description => 'AI profile to use Cohere for SQL translation' ); END;
Set profile for DB session.
EXEC DBMS_CLOUD_AI.set_profile('CohereDemoProfile');
Now we are ready to use SELECT AI.
Run below SQL command to provide prompt in natural language:
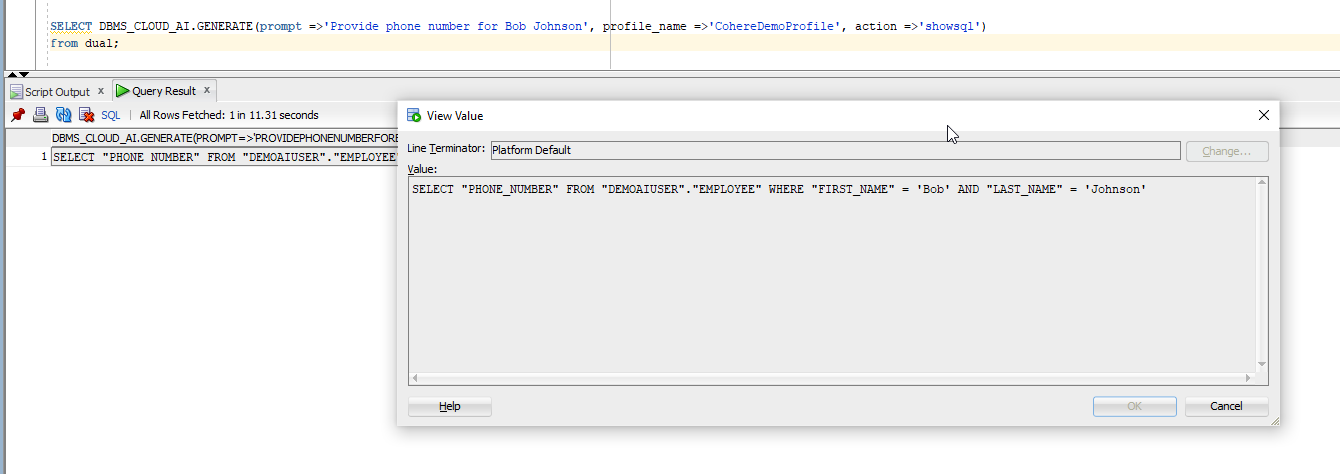
SELECT dbms_cloud_ai.generate( prompt => 'Provide phone number for Bob Johnson', profile_name => 'CohereDemoProfile', action => 'showsql' ) FROM dual;
Result: